| << Previous (Modelling) | (Installation) Next >> |
ST7-R3.57 Theory |
||
|---|---|---|
| ST7-R3.57.10 Theory / Materials | ||
|
1.0 MB |
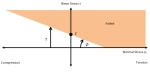
ST7-R3.57.10.1 Mohr-Coulomb Yield Criterion The Mohr-Coulomb yield criterion is often used in the analysis of frictional materials such as soil and concrete. The behaviour of these materials is governed by material cohesion and the internal friction angle. In this Webnote we develop the equations used by Strand7 to calculate failure and produce results using this yield criterion. |
|
|
1.1 MB |
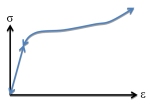
ST7-R3.57.10.3 Nonlinear Elastic Material This Webnote gives an overview of the behaviour of the nonlinear elastic material model. Worked examples are included to illustrate the calculations undertaken by the solver. |
|
|
1.0 MB |
ST7-R3.57.10.5 Elastic and Plastic Strain This Webnote gives an overview of elastic and plastic strain as reported in the Strand7 plate and brick elements for material nonlinear analysis. An elasto-plastic material with the von Mises yield criterion and isotropic hardening is used to illustrate these quantities. |

|
| ST7-R3.57.30 Theory / Solvers | ||
|
1.0 MB |
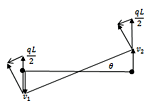
ST7-R3.57.30.14 Follower Loads for Linear Buckling and Natural Frequency Solvers Pressure loads on a surface “follow” the surface as it deforms; i.e., the direction of the resultant of the pressure follows the changing direction of the surface normal. This follower effect can lead to a reduction in buckling load and can modify natural frequencies. The linear buckling and natural frequency solvers, using the elastic and the stress stiffness matrices, do not capture this effect, and therefore the Nonlinear Static and/or Nonlinear Transient Dynamic solvers, with geometric nonlinearity, are usually required. Alternatively, the follower load option, available in the Strand7 Linear Buckling and Natural Frequency solvers, can be used to add a “load stiffness” term that depends on the geometry change to account for the follower effect. |
|
| << Previous (Modelling) | (Installation) Next >> |

 Menu
Menu